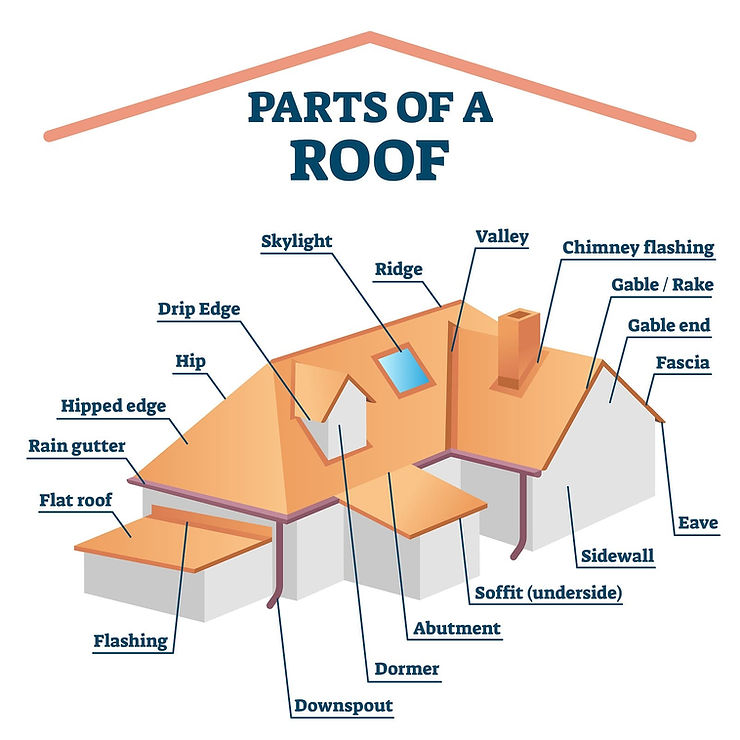
Use this glossary as a quick reference as you navigate your roofing job.
A
- Asphalt Shingles: Common roofing material made from asphalt for waterproofing.
- Apron Flashing: A term for metal flashing used at chimney fronts.
B
- Barge Board: A board fastened to the projecting gables of a roof.
- Bitumen: A black, sticky substance used in certain roofing materials.
C
- Cricket: A peaked water diverter installed behind chimneys or along roof ridges.
- Counterflashing: Metal flashing that's installed to prevent moisture entry.
D
- Decking: The substrate over which roofing is applied, usually plywood or OSB.
- Dormer: A protruding mini-roofed structure with a window.
E
- Eaves: The lower border of the roof that overhangs the walls.
- EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer): A durable synthetic rubber roofing membrane.
F
- Flashing: Materials used to waterproof a roof around any projections.
- Fascia: A board that runs along the roof's edge, connecting the roof and the outer walls.
G
- Gable: The triangular portion of a wall between the edges of intersecting roof pitches.
- Granules: Mineral particles coated on the surface of shingles.
H
- Hip Roof: A roof with sloping ends and sides.
- HVAC Penetrations: Vents or exhausts for heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems.
I
- Ice Dam: A ridge of ice that forms at the edge of a roof and prevents melting snow from draining.
- Insulation: Material used to keep heat in or out of a home.
J
- Joist: Horizontal structures that support the decking.
- J-Channel: A type of trim used around windows and doors on the roof.
K
- Kick-Out Flashing: Flashing that diverts water away from the cladding.
L
- Laminated Shingles: Shingles containing more than one layer of material for durability.
- Louvers: Slatted devices installed in a gable or soffit for ventilation.
M
- Membrane: A type of roofing system for flat roofs, made from modified bitumen.
- Mansard Roof: A four-sided gambrel-style hip roof.
N
- Nesting: Installing a new layer of shingles over an old layer.
- NRCA (National Roofing Contractors Association): An association that represents all aspects of the roofing industry.
O
- Overhang: The portion of the roof structure that extends beyond the exterior walls.
- OSB (Oriented Strand Board): A type of decking material made from compressed wood strands.
P
- Pitch: The angle or slope of a roof.
- Ply: A layer of roofing (in felt, ply sheet, etc.).
Q
- Quarter Sawn: A type of wood cut that's less likely to warp.
R
- Rafter: The supporting framing to which the roof deck is attached.
- Ridge: The top edge of two intersecting sloping roof surfaces.
S
- Soffit: The exposed surface beneath the overhanging section of a roof eave.
- Shingle: A piece of roofing material that is laid in overlapping rows.
T
- Tar: A black, viscous material used in roofing.
- Truss: A framework, typically consisting of rafters, posts, and struts, supporting a roof.
U
- Underlayment: A layer of material placed beneath shingles to provide additional protection.
V
- Valley: The internal angle formed by the intersection of two sloping roof planes.
- Vapor Barrier: Material used to prevent moisture from penetrating the roof.
W
- Warranty: A promise by the manufacturer or roofer regarding the quality and performance of roofing materials or work.
- Weep Holes: Small openings that allow for water drainage.
X
- Xactimate: A software used for estimating construction and repair costs, commonly in roofing.
Y
- Yield Point: The point at which a material begins to deform permanently.